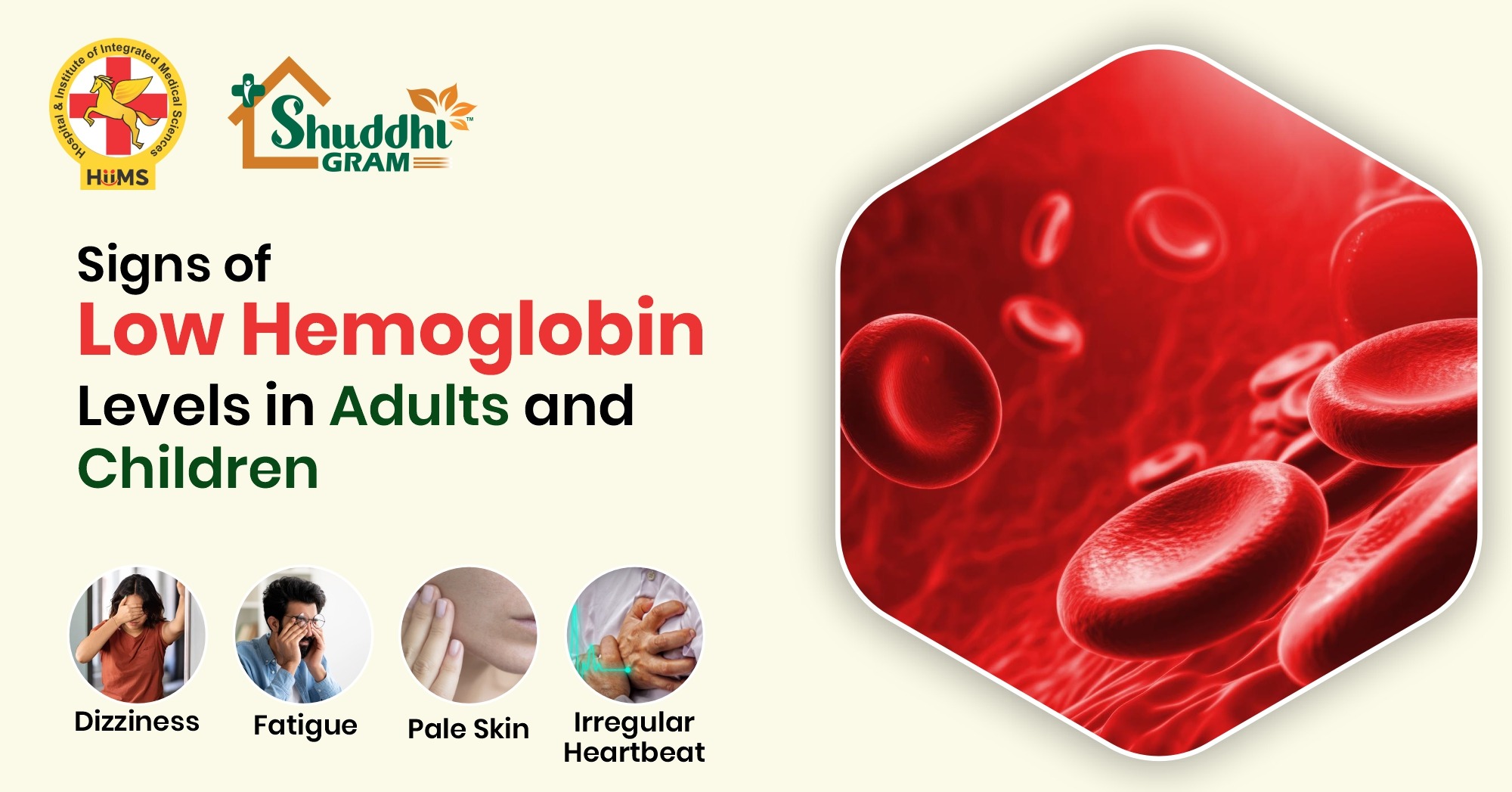
Hemoglobin is a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen all over the body. If hemoglobin levels become low, the body does not get enough oxygen, and this can cause different health problems. It is important to notice low hemoglobin symptoms early so the condition can be managed on time. Low hemoglobin can affect both adults and children, but the signs may look different depending on age, health, and how serious the problem is.
Recognizing the low hemoglobin signs in adults is essential because fatigue, weakness, or pale skin are often dismissed as everyday tiredness. Similarly, children may show different signals that need close attention, such as irritability or slower growth. Since hemoglobin plays such an important role, knowing how to identify these changes helps families take timely action.
In this article, we will look closely at the common symptoms, age-specific signs, and what causes low hemoglobin, making it easy for you to understand and act responsibly.
What Are Low Hemoglobin Symptoms?
Low hemoglobin directly impacts how well oxygen is delivered to the tissues and organs. This deficiency usually leads to observable alterations in the body. Common symptoms include:
- Regular exhaustion or sleepiness despite a good rest.
- Shortness of breath during simple activities.
- Dizziness or lightheadedness.
- Unusual paleness of skin, lips, or nail beds.
- Cold feet and hands because of low oxygen circulation.
These low hemoglobin symptoms can occur slowly, and most individuals mistake them for stress or insomnia. But when these signs continue, they cannot be disregarded.
Signs of Low Hemoglobin in Adults
Adults are more likely to ignore health signals because they often attribute them to lifestyle issues. Some of the specific signs of low hemoglobin in adults include:
- Extreme fatigue and weakness: Energy levels drop drastically, making daily activities harder.
- Rapid heartbeat: The heart works harder to supply oxygen when hemoglobin is low.
- Chest discomfort: Some adults may feel chest heaviness when oxygen supply is insufficient.
- Headaches and difficulty concentrating: Lack of oxygen affects brain function, leading to poor focus.
These symptoms can impact work, productivity, and overall well-being if not addressed promptly.

Signs of Low Hemoglobin in Children
Children display different symptoms compared to adults. Parents and caregivers should be observant of any unusual changes. Common signs of low hemoglobin in children include:
- Slow growth and development: Insufficient hemoglobin can delay physical and mental development.
- Frequent irritability or mood swings: Low oxygen supply can make children restless and easily upset.
- Poor appetite: Many children with this condition may refuse food or eat less than usual.
- Paleness: Their face, gums, or inner eyelids may look noticeably pale.
- Frequent infections: A weakened system may struggle to fight illnesses.
Spotting these signs early allows parents to consult a professional and make necessary dietary and lifestyle changes.
What Causes Low Hemoglobin?
Several factors can contribute to this condition. Knowing the causes of low hemoglobin is important for prevention and care. Common reasons include:
- Nutritional deficiencies: Lack of iron, vitamin B12, or folic acid directly affects hemoglobin production.
- Blood loss: Heavy menstruation, injuries, or internal bleeding can decrease levels.
- Chronic illnesses: Kidney disease, liver problems, or other long-term conditions often lower hemoglobin.
- Inherited conditions: Some genetic disorders, such as thalassemia, can affect red blood cell production.
- Rapid growth in children: During growth spurts, children may need higher nutrition, and a deficiency can lead to lower hemoglobin.
Understanding the root cause ensures that the right measures are taken to restore balance.
How to Identify and Address Symptoms Early
While symptoms vary, being alert to the early signs can help prevent complications. Adults should pay attention to persistent tiredness, shortness of breath, or chest discomfort. Parents should monitor children for changes in appetite, growth, or irritability. A blood test is usually recommended to confirm low hemoglobin levels.
Alongside medical advice, maintaining a diet rich in iron-containing foods like leafy greens, legumes, nuts, and whole grains can increase hemoglobin. Including vitamin C-rich foods also helps the body absorb iron better.
Conclusion
Low hemoglobin can affect anyone, whether it’s a child or an adult, but if you know the symptoms, you may control it on time. In adults, feeling very tired or dizzy can be a warning sign, while in children, slow growth and crankiness may point to low hemoglobin symptoms. Low levels may happen due to poor diet, blood loss, long-term illness, or inherited conditions, so noticing the warning signs matters. A simple blood test can confirm the condition, and with timely awareness and the right steps, you can safeguard your health and well-being.
 Reviewed by Dr. Jayant Batra (BAMS,PDBM,PGDCC,M.A.,YOGA)
Reviewed by Dr. Jayant Batra (BAMS,PDBM,PGDCC,M.A.,YOGA)





No approved comments yet.